Vincent's angina
Background
- Fusospirochetal infection of the pharynx and palatine tonsils, causing "ulcero-membranous pharyngitis and tonsillitis"[1]
- Same pathogenic organisms as acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG)
- Vincent's angina is sometimes confused with ANUG, but the former is tonsillitis and pharyngitis, and the latter involves the gums
Clinical Features[2]
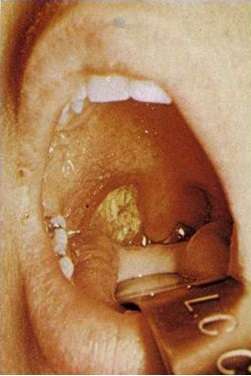
Pseudomembrane of right tonsil.
- Superficial ulceration and necrosis of the tonsils and pharynx that often results in formation of a pseudomembrane
- Foul smelling breath
- Odynophagia
- Submandibular lymphadenopathy
- Exudate
- Patients typically have poor oral hygiene
Differential Diagnosis
Bacterial infections
- Streptococcal pharyngitis (Strep Throat)
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Diphtheria (C. diptheriae)
- Bacterial Tracheitis
Viral infections
- Infectious mononucleosis (EBV)
- Patients with peritonsillar abscess have a 20% incidence of mononucleosis [3]
- Laryngitis
- Acute Bronchitis
- Rhinovirus
- Coronavirus
- Adenovirus
- Herpesvirus
- Influenza virus
- Coxsackie virus
- HIV (Acute Retroviral Syndrome)
Other
- Deep neck space infection
- Peritonsillar Abscess (PTA)
- Epiglottitis
- Kawasaki disease
- Penetrating injury
- Caustic ingestion
- Lemierre's syndrome
- Peritonsillar cellulitis
- Lymphoma
- Internal carotid artery aneurysm
- Oral Thrush
- Parotitis
- Post-tonsillectomy hemorrhage
- Vincent's angina
- Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
Evaluation
- Diagnosis based on clinical findings and gram stain
Management
- Organisms involved are polymycrobial but often include Fusobacterium necrophorum, Treponema, Selenomonas, and Prevotella
Uncomplicated Disease
- Amoxicillin 250mg 3 x daily for 7 days AND/OR
- Metronidazole 250mg 3 x daily for 7 days[4]
Complicated Disease
- Penicillin V 500mg PO q6 hours PLUS metronidazole 500mg PO q8 hours x 10 days OR
- Amoxicillin 500mg PO TID PLUS metronidazole 250mg PO TID for 10d OR
- Amoxicillin-clavulanate 500mg/125mg PO TID or 875mg/125mg PO BID for 10d OR
- Clindamycin 150-300mg PO TID for 10d OR
- Doxycycline 100mg PO BID for 10d[5]
Disposition
External Links
References
- Taylor, FE; McKinstry, WH (1917). "The Relation of Peri-dental Gingivitis to Vincent's Angina." Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine. 10 (Laryngol Sect): 43–8.
- Marx, J. A., Hockberger, R. S., Walls, R. M., & Adams, J. (2002). Rosen's emergency medicine: Concepts and clinical practice. St. Louis: Mosby.
- Melio, Frantz, and Laurel Berge. “Upper Respiratory Tract Infection.” In Rosen’s Emergency Medicine., 8th ed. Vol. 1, n.d.
- Atout R. N. et al. Managing Patients with Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis. J Can Dent Assoc 2013;79:d46. http://www.jcda.ca/article/d46. Accessed April 2015
- Stephen J. et al Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis Empiric Therapy. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2028117-overview. Accessed April 2015
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.