Ventriculoperitoneal shunt overdrainage
Background
- Overdrainage → tissue occluding the orifices of the proximal shunt apparatus
- As pressure increases the occluding tissue diesengages allowing drainage to resume
- Leads to cyclic increased ICP complaints that worsen when patient stands
- Newer valve devices with antisiphon features make this less common
Clinical Features
- Vague symptoms of dizziness, visual disturbances
- Worsened with standing/exertion
Differential Diagnosis
Evaluation
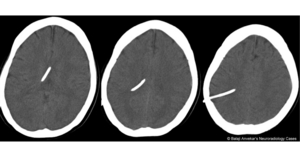
- CT head necessary for shunt placement workup and over-drained ventricles
- Patients at higher risk for subdural hematomas
Management
- Neurosurgery consult
Disposition
- Admission for shunt revision versus valve adjustment
See Also
External Links
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.