Tympanic membrane rupture
Background
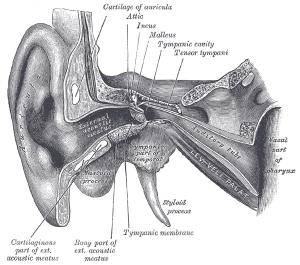
Ear anatomy
Causes
- Blunt trauma (hand blow to ear, fall, direct hit)
- Penetrating trauma (Q-tip, matchstick, gunshot wound, welding spark)
- Direct ear trauma
- Lightning strike
- Barotrauma
- Blast injury
- Air travel
- Scuba diving
Clinical Features
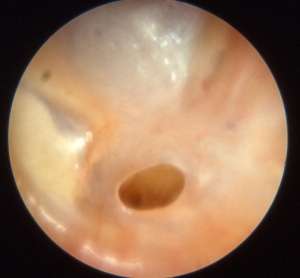
Smaller perforation
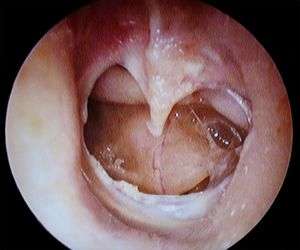
Larger perforation (acute)
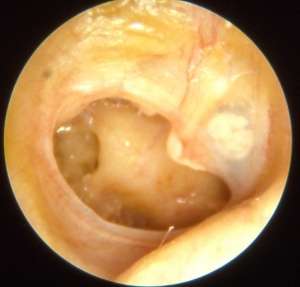
Larger perforation (chronic)
- Ear pain
- History of barotrauma or direct ear trauma
- May also have:
Differential Diagnosis
External
- Auricular hematoma
- Auricular perichondritis
- Cholesteatoma
- Contact dermatitis
- Ear foreign body
- Herpes zoster oticus (Ramsay Hunt syndrome)
- Malignant otitis externa
- Otitis externa
- Otomycosis
- Tympanic membrane rupture
Inner/vestibular
Evaluation
- Typically clinical
Management
- Isolated small tympanic membrane perforations
- Antibiotic ear drops for contaminated wounds - ciprofloxacin suspension (more appropriately viscous than solution)
- Water precautions (keeping water out of the middle ear), avoid forceful Valsalva
- Reevaluation with PCM, typical healing within 4-6 weeks
- In children after TM perforation due to otitis media, PO antibiotics preferred over topical
- Significant hearing loss (≥40 dB), vertigo, nystagmus, ataxia, facial nerve injury, large perforation with folded over edges, prolonged healing
- Urgent evaluation by ENT
Disposition
- Outpatient management
See Also
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.