Trichomonas vaginalis
Background
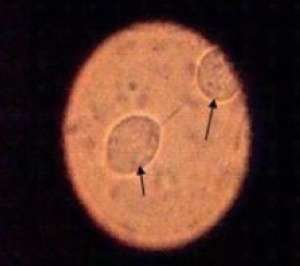
Wet mount of trichomonas. Note oval/pear shape with conspicuous flagella.
Clinical Features
- Yellow/green, malodorous vaginal discharge
- Vaginal erythema or edema
- "Strawberry Cervix" on speculum examination.
Differential Diagnosis
Evaluation
- Wet mount shows mobile trichomonads
Management
Pregnant
Only treat if the patient is symptomatic and avoid breast feeding until 24-hrs after last dose
- Metronidazole 2g PO once[3]
Disposition
- Outpatient
See Also
References
- Mavedzenge SN, Pol BV, Cheng H, Montgomery ET, Blanchard K, de Bruyn G, Ramjee G, Straten Av. Epidemiological synergy of Trichomonas vaginalis and HIV in Zimbabwean and South African women. Sex Transm Dis. 2010 Jul;37(7):460-6. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3181cfcc4b. PubMed PMID: 20562586.
- Kissinger P et al. Single-dose versus 7-day-dose metronidazole for the treatment of trichomoniasis in women: An open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2018 Oct 5; [e-pub].
- CDC Trichomoniasis 2015. https://www.cdc.gov/std/tg2015/trichomoniasis.htm
- CDC. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines. MMWR Recomm Rep 2010;59(No. RR-12)
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.