Thromboangiitis obliterans
Background
- Also known as "Buerger's disease"
- Idiopathic inflammatory occlusive disease of the hands and feet (exact pathogenesis unknown)
Risk factors
- Tobacco use
- Virtually all affected patients are smokers
- Male
- Middle Eastern
Clinical Features
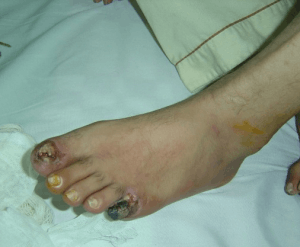
Thromboangiitis obliterans of foot
- Red, tender nodules over peripheral arteries
- May have diminished pulses
- In-step claudication
- Hand claudication
- Often bilateral and symmetrical
- May lead to ulceration
- Raynaud phenomenon
- Gangrene and autoamputation of digits in severe disease
Differential Diagnosis
Blue Digit
- Acute peripheral artery disease
- Atheroembolism (AKA Blue Toe Syndrome)
- Arterial embolism
- Arterial thrombosis
- Vasospastic Disorders
- Raynaud’s disease
- Primary erythromelalgia
- Autoimmune
- Idiopathic
- Thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger's disease)
- Chronic peripheral artery disease
- Atherosclerosis obliterans
Evaluation
- Clinical criteria for diagnosis (noninvasive testing not necessary)
- History of smoking
- Onset prior to <50 years old
- Absence of atherosclerotic risk factors
- Upper limb involvement
- Infrapopliteal arterial occlusive lesions
Management
- Abstinence from tobacco
- Early symptoms with out threatened tissue loss: outpatient vascular
- Advanced disease: intra-arterial or intravenous PGE1, ASA, Heparin, arterial reconstruction, sympathectomy
Disposition
- Discharge with vascular follow-up if no evidence/threat of tissue loss
- Otherwise admit
See Also
External Links
References
Video
START_WIDGETcda64ca5df638f3d-0END_WIDGET
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.