Spinal stenosis
Background
Clinical Features
- Lower back pain that gets progressively worse over time
- Pain relieved with forward flexion (walking uphill)
- Pain worse with extension (walking downhill)
Differential Diagnosis
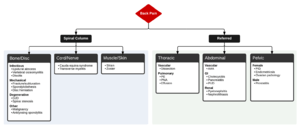
Differential diagnosis of back pain
Lower Back Pain
- Spine related
- Acute ligamentous injury
- Acute muscle strain
- Disk herniation (Sciatica)
- Degenerative joint disease
- Spondylolithesis
- Epidural compression syndromes
- Spinal fracture
- Cancer metastasis
- Spinal stenosis
- Transverse myelitis
- Vertebral osteomyelitis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Spondylolisthesis
- Discitis
- Renal disease
- Kidney stone
- Pyelonephritis
- Nephrolithiasis
- Intra-abdominal
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Ulcer perforation
- Retrocecal appendicitis
- Large bowel obstruction
- Pancreatitis
- Pelvic disease
- PID
- Other
Evaluation
- Check ankle-brachial index (ABI) to rule out vascular claudication
Management
- Avoid alcohol and strengthen legs to prevent falls
- Exercise bike or walking recommended with rest when pain comes
- Pain control
Disposition
- If no cauda equina and pain controlled → outpatient
- As outpatient, can consider referral for decompressive laminectomy for severe persistent pain
See Also
External Links
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.