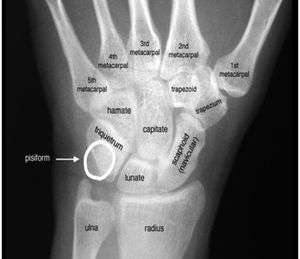
Scaphoid fracture
Background
- Most commonly fractured carpal bone
- Occurs via FOOSH or axial load directed along thumb's metacarpal
- Most common fracture at the waist of the scaphoid
- Avascular necrosis
- Most commonly associated with proximal fractures (blood supply enters the distal part of the bone)
Clinical Features
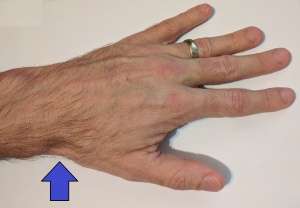
Anatomical snuff box
- Pain along radial aspect of wrist
- Localized tenderness in anatomic snuffbox
- Pain elicited by axial pressure directed along thumb's metacarpal
Differential Diagnosis
Evaluation
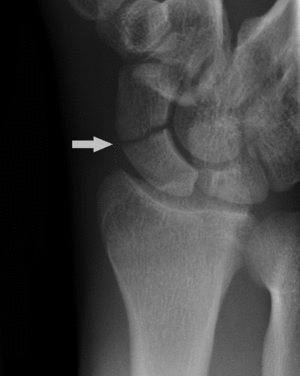
Scaphoid waist fracture
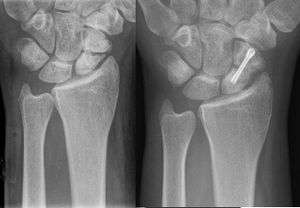
Scaphoid pseudarthrosis, before and after treatment with Herbert screw.
Workup
- X-ray
- Obtain both standard and scaphoid views
- Up to 10% of initial radiographs fail to detect a fracture
- MRI
- Gold-standard in cases in which high index of suspicion remains despite negative x-ray
Diagnosis
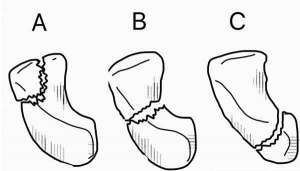
Scaphoid fractures occur in three locations: (A) Distal tubercle, (B) waist, and (C) proximal pole.
- Assess for instability:
- Oblique fracture
- >1mm of displacement
- Rotation
- Comminution
- Carpal instability pattern is present
Management
All patients with clinical suspicion should be treated regardless of x-ray findings
General Fracture Management
- Acute pain management
- Open fractures require immediate IV antibiotics and urgent surgical washout
- Neurovascular compromise from fracture requires emergent reduction and/or orthopedic intervention
- Consider risk for compartment syndrome
Immobilization
- Stable fracture: short-arm thumb spica splint in dorsiflexion and radial deviation
- Unstable fracture: long-arm thumb spica splint
Disposition
- Refer to a hand surgeon because may lead to osteonecrosis if not properly recognized/treated
- 25% of those with initially neg xray will actually have a fracture (typically found on delay xray or other modality)[1]
- Repeat Wrist and scaphoid X-rays should be obtained 2-3 weeks after initial injury to assess for fracture if suspicion is high.
- Immobilization may be required for at least 6-12 wks
See Also
References
- Gemme S and Tubbs R. What Physical Examination Findings and Diagnostic Imaging Modalities Are Most Useful in the Diagnosis of Scaphoid Fractures? Annals of Emergency Medicine. 2015. 65(3):308-309.
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.