Scabies
Background
- Infestation with the Sarcoptes scabiei mite
- 4-6 week incubation period after initial exposure
- Those previously infected, symptoms begin in 1-3 days (sensitization)
- Type IV hypersensitivity
- Not a reflection of poor hygiene
Clinical Features
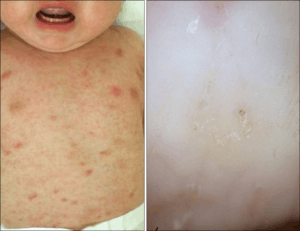
Traditional infantile scabies.

10-X magnification showing numerous scabies heads (arrows).
Scabies
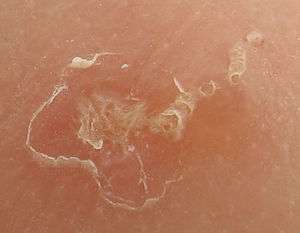
Scabies burrow at high resolution
Seek history of symptomatic close contacts (human or animal)
Infants
- Hyperpigmented nodules, vesiculopustules, papules may be found in axilla and diaper areas
- May be generalized
Older children / adults
- Generalized eruption with linear burrows, papules, pustules
- Predominance in web spaces of the fingers, flexor aspect of the wrists, axillae, groin, nipples, and the periumbilical region
- Pruritus is classically worse at night
Norwegian Scabies
- In immunocompromised
- Severe disease with diffuse scabies
- Requires multiple treatments
Differential Diagnosis
Domestic U.S. Ectoparasites
- Bed bugs
- Lice
- Scabies (Mites)
- Ticks
- Fleas
- Pseudoparasites
- Delusional parasitosis (Ekbom syndrome)
See also travel-related skin conditions
Evaluation
- Clinical diagnosis, based on history and physical exam
Management
General Care
- Wash all linens/clothes in hot water or bag bulky items and keep sealed for 2wks
- Pruritus may continue for weeks despite successful elimination of infestation
- Consider steroids for symptom relief
Adults
- Permethrin 5% cream for all family members[1]
- Apply from neck down
- Leave on for 8-12hr before washing off
- Has 95-98% success rate, may reapply in 1-2wks if incomplete effect
- Ivermectin 200 mcg/kg may be necessary for severe infection
- Also viable option in adolescent or adult with insecure social situation
- Success rate 70%, increases if give repeat dose 2wks after
- Contraindicated in lactating women and children < 15kg
Infants
- Permethrin 5% is FDA approved for > 2 months of age although still recommended for neonatal scabies[2]
- May require application head to toe (avoid mucus membranes)
- Leave on for 8-12 hours, then wash off
Avoid
- Lindane - effective treatment but associated with potential for toxic manifestations (seizures, neurotoxicity)
- Reserved for refractory cases
Disposition
- Discharge
References
- Strong M. Johnstone P. Interventions for treating scabies. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;(3):CD000320
- Subramaniam S. Rutman MS. Wnger JK. A papulopustular, vesicular, crusted rash in a 4-week old neonate. Pediatric Emergency Care. 2013;29:1210-1212
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.