Retroperitoneal hemorrhage
Background
- Bleeding into retroperitoneal space
- Difficult to diagnose given poor sensitivity of physical exam findings (Cullens, Grey-Turners)
- Can accumulate 4L blood before tamponade
Etiologies
- Trauma (renal, vascular, colon, pancreas or pelvis)
- Leaking/ruptured AAA
- Iatrogenic (colonoscopy, cardiac catheterization, femoral line placement)
- Spontaneous (coagulopathy)
- Hemorrhagic pancreatitis
Clinical Features
- Most common in patients with bleeding disorders, on anticoagulants, and on HD[1][2]
- May present with:
- Abdominal pain
- Flank pain
- Back pain
- Hypotension
- Bryant's sign (unilateral scrotal ecchymosis from tracking blood)
Differential Diagnosis
Evaluation
Workup
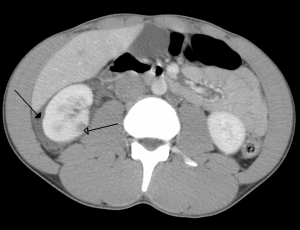
Right kidney contusion (open arrow) and blood surrounding the kidney (closed arrow).
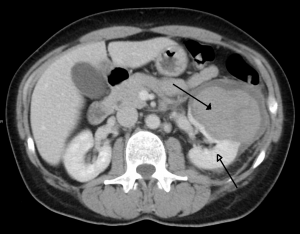
Left kidney injury (open arrow) with retropeitoneal hematoma (closed arrow).
Must have high clinical suspicion to make diagnosis
- CT scan abdomen/pelvis
- Consider ultrasound for AAA
- FAST and DPL do not evaluate retroperitoneal space
Classification of traumatic retroperitoneal hemorrhage[3]
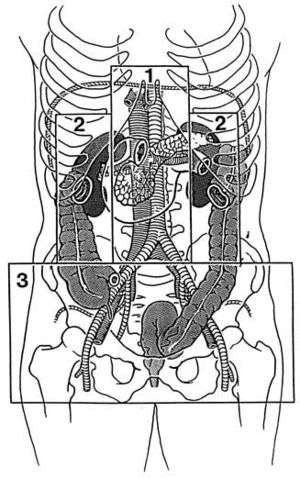
- Zone 1: Central
- Pancreaticoduodenal injuries, major vascular injury
- Zone 2: Flank/Perinephric
- Renal trauma, ureteric or colonic injury
- Zone 3: Pelvic
- Pelvic fracture or ileofemoral vascular injury
Management
- Address A, B, C's
- Resuscitation with blood products
- Reverse coagulopathy
- Warfarin (Coumadin) Reversal
- Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Reversal
- Unfractionated heparin reversal
- Treat underlying etiology
Disposition
- ICU
See Also
- Abdominal trauma
- coagulopathy
- Warfarin (Coumadin) Reversal
- Dabigatran (Pradaxa) Reversal
- Unfractionated heparin reversal
- Aortic ultrasound
External Links
References
- Bhasin HK and Dana CL. Spontaneous retroperitoneal hemorrhage in chronically hemodialyzed patients. Nephron. 1978; 22(4-6):322-327.
- Ernits M, et al. A retroperitoneal bleed induced by enoxaparin therapy. Ann Surg. 2005; 71(5):430-433.
- FELICIANO, D. V. (1990) ‘Management of Traumatic Retroperitoneal Hematoma’, Annals of Surgery, 211(2), pp. 109–123.
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.