Raynaud’s disease
Background
- Exaggerated vascular response to cold or emotional stress
Clinical Features
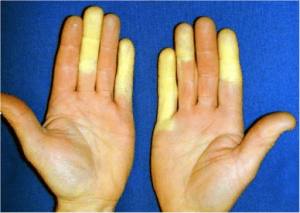
Raynaud Phenomenon
- Sharp demarcated color changes of the skin of the digits
- Pain, loss of sensation, and if recurrent ischemia may cause ulcers
Differential Diagnosis
- Primary (Raynaud disease or idiopathic Raynaud Phenomenon)
- Symptoms without an associated disorder
- Secondary (associated with another illness, i.e. SLE or Scleroderma)
Evaluation
- Assess for digital ischemia
- Consider evaluation for underlying disorder
Management
Improve quality of life and prevent ischemic tissue injury
- Patient education on trigger avoidance
- Severe cases/Ischemia
- Pharmacologic
- Oral vasodilators
- Nifedipine 30 to 180 mg/day
- Amlodipine 5 to 20 mg/day
- Topical nitrates
- Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors
- Oral vasodilators
- Surgical sympathetic blockade
- Pharmacologic
Disposition
Patient with digital ischemia not responsive to oral or topical vasodilators may need anticoagulants, IV prostanoids, and sympathectomy
See Also
External Links
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.