Quadriceps tendon rupture
Background
- Occurs via forceful contraction of quadriceps muscle or falling on flexed knee
- Typically occur 2cm from insertion on patella
Clinical Features
- Sudden "pop" or tearing
- Diffuse swelling
- Defect may be palpable above the patella
- Partial tears lead to difficulty extending the knee
- Complete tears lead to absent straight leg raise while supine or extension of the knee again
Differential Diagnosis
Acute knee injury
- Knee dislocation
- Knee fractures
- Meniscus and ligament knee injuries
- Patella dislocation
- Patellar tendonitis
- Patellar tendon rupture
- Quadriceps tendon rupture
Nontraumatic/Subacute
- Arthritis
- Gout and Pseudogout
- Osgood-Schlatter disease
- Patellofemoral syndrome (Runner's Knee)
- Patellar tendonitis (Jumper's knee)
- Pes anserine bursitis
- Popliteal cyst (Bakers cyst)
- Prepatellar bursitis (nonseptic)
- Septic bursitis
- Septic joint
- DVT
Evaluation
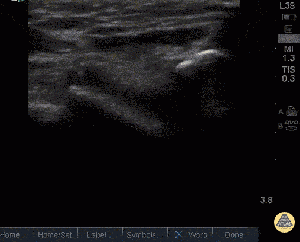
Quadriceps tendon rupture[1]
- Ultrasound
- Separation of the tendon can be visualized
- X-ray
- Patella baja/infera (low-riding patella)
Patellar vs Quadriceps tendon rupture
| Finding | Patellar tendon rupture | Quadriceps tendon rupture |
| Location | Distal to patella | Proximal to patella |
| Typical group | Patients <40yr with history of tendinitis or steroid injections | Patients >40yr |
| X-ray | Patella alta (high-riding patella) | Patella baja/infera (low-riding patella) |
Management
- Ortho consult in the ED
- Knee immobilizer, can be weight bearing
- Operative repair advised within 7 days
Disposition
- Outpatient
See Also
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.