Pilon fracture
Background
- High energy axial loading injury that drives tibial plafond (French for ceiling) into talar dome
- Motor vehicle accidents, falls from height
- "Pilon" is another word for pestle, a tool used to grind substance in a mortar
- Also known as a tibial plafond fracture
Clinical Features
- Ankle pain/deformity
- Inability to bear weight
- Local tenderness to palpation
Differential Diagnosis
Evaluation
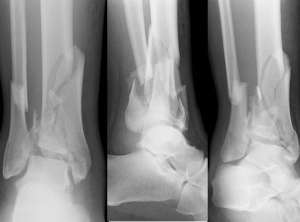
Pilon fracture
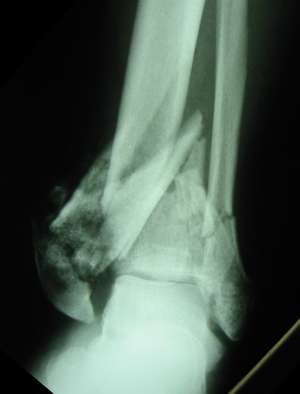
Pilon Fracture
Work-Up
- Plain radiographs
- AP, Lateral, and Mortise views of ankle
- CT often necessary to reveal amount of articular surface displacement/develop treatment plan
Diagnosis
- Assess distal pulse, motor, and sensation
- Inspect skin for signs of open fracture
- Suspect other fracture as well, given mechanism:
- Lumbar spine (esp L1), calcaneus, talar dome, tibial plateau, femoral neck, acetabulum,
- Monitor for compartment syndrome
Management
General Fracture Management
- Acute pain management
- Open fractures require immediate IV antibiotics and urgent surgical washout
- Neurovascular compromise from fracture requires emergent reduction and/or orthopedic intervention
- Consider risk for compartment syndrome
Specific Management
- Long leg posterior splint
- Consult ortho for surgery
Disposition
- If stabilized without evidence of significant articular displacement, can be managed as outpatient after consultation with Ortho
Admit for
- Open fracture
- Signs of neurovascular compromise
- Concern for compartment syndrome
See Also
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.