Patella fracture
Background
- Occurs via direct blow or forceful contraction of quadriceps muscle
- Do not confuse a bipartite patella with a fracture
Clinical Features
- Focal patellar tenderness, swelling, effusion
- Check integrity of knee extensor mechanism by having patient perform straight-leg raise
Differential Diagnosis
Acute knee injury
- Knee dislocation
- Knee fractures
- Meniscus and ligament knee injuries
- Patella dislocation
- Patellar tendonitis
- Patellar tendon rupture
- Quadriceps tendon rupture
Nontraumatic/Subacute
- Arthritis
- Gout and Pseudogout
- Osgood-Schlatter disease
- Patellofemoral syndrome (Runner's Knee)
- Patellar tendonitis (Jumper's knee)
- Pes anserine bursitis
- Popliteal cyst (Bakers cyst)
- Prepatellar bursitis (nonseptic)
- Septic bursitis
- Septic joint
- DVT
Evaluation
Imaging
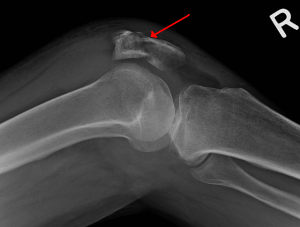
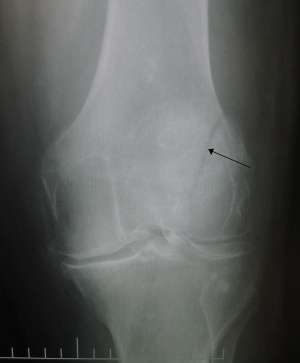
- AP and lateral
- Lateral view: Distance from tibial tubercle:lower pole of patella ~ length of patella +/- 20%
- If greater than this suspect patellar ligament rupture
- Lateral view: Distance from tibial tubercle:lower pole of patella ~ length of patella +/- 20%
- Consider skyline (sunset) view if suspect fracture of articular surface
Management
- Nondisplaced with intact extensor mechanism: knee immobilizer, rest, ice
- Displaced >3mm or disruption of extensor mechanism: above + early referral for ORIF
Disposition
- Outpatient
See Also
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.