Olecranon bursitis (nonseptic)
Background
- Inflamation of the bursal cavity superficial to the olecranon
- Majority of cases are not infectious, but inflammation can be from infection (septic bursitis)
- Also known as "student's elbow" or "baker's elbow"
- Often caused by repeated minor trauma from external pressure to elbow
- There is controversy regarding initial diagnosis and treatment[1]
Clinical Features
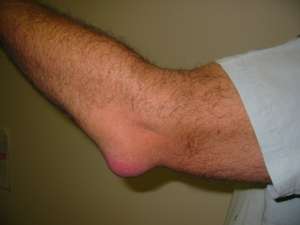
Olecranon bursitis, nonseptic
- Bursal fluid on exam
- Non-erythematous
- FROM
- Negative axial load
Differential Diagnosis
Radiograph-Positive
- Distal humerus fracture
- Radial head fracture
- Capitellum fracture
- Olecranon fracture
- Elbow dislocation
Radiograph-Negative
- Lateral epicondylitis
- Medial epicondylitis
- Olecranon bursitis (nonseptic)
- Septic bursitis
- Biceps tendon rupture/dislocation
Evaluation
- Xrays if trauma, may consider for all to rule out bone spur as causative agent (although not emergent)
- Initial aspiration is controversial[2]. There is currently no consensus on the optimal diagnosis strategy for prepatellar bursitis. The majority of patients studied did receive an aspiration of fluid (82%), but those patients had a significantly higher rate of complications (persistent infection, secondary infection in initially aseptic bursae) than patients treated with antibiotics alone.[3]
- If any signs of infection, must aspirate to rule out septic bursitis
- If no signs of infection:
- May consider initial conservative (no aspiration) treatment for several days[4]
- Some sources suggest aspiration for all cases
Management
- Acute
- Avoid trauma and excessive pressure
- RICE & NSAIDs
- Chronic = surgery
Disposition
- Outpatient management
See Also
References
- Blackwell1 JR, et al. Olecranon bursitis: a systematic overview. Shoulder & Elbow; 2014, Vol. 6(3) 182–190. DOI: 10.1177/1758573214532787
- Blackwell1 JR, et al. Olecranon bursitis: a systematic overview. Shoulder & Elbow; 2014, Vol. 6(3) 182–190. DOI: 10.1177/1758573214532787
- Baumbach SF et al. Prepatellar and Olecranon bursitis: literature review and development ofa treatment algorithm. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. (2014) 134: 359 - 370.
- Blackwell1 JR, et al. Olecranon bursitis: a systematic overview. Shoulder & Elbow; 2014, Vol. 6(3) 182–190. DOI: 10.1177/1758573214532787
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.