Molluscum contagiosum
Background
- Self-limited skin condition caused by Molluscum Contagiosum Virus, member of poxvirus family
- Most common in children 0-14 years of age [1]
- Also affects sexually active adults and immunocompromised patients[2]
- Transmitted via direct contact (including sexual contact) or fomites
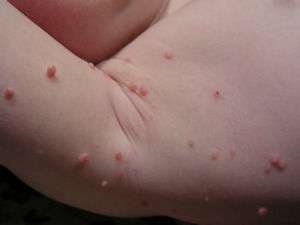
Molluscum contagiosum lesions on an arm
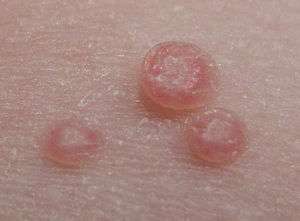
Molluscum contagiosum at higher magnification
Clinical Features
- Begins as painless, small papule
- Becomes raised, pearly, flesh-colored dome with central umbilication (called "mollusca")[2]
- Cental umbilication contains plug of virus-filled white caseous material.
- Can be solitary or multiple
- Can affect any part of the body
- Genital mollusca on pediatric patients should prompt concern for child abuse
- Auto-innoculation is also possible[3]
- Genital mollusca on pediatric patients should prompt concern for child abuse
Differential Diagnosis
Evaluation
- Clinical diagnosis, based on history and physical examination
- Biopsy with histology can confirm diagnosis if unclear
Management
- Hygiene is key to reduce spread
- Ensure adequate hand-washing
- Wash all clothes in warm water
- Avoid touching the area
- Avoid sharing towels or clothing
- Self-limited - no specific treatment necessary
- Lesions resolve within 6-18 months in immunocompetent patients[2]
- Treatment may be warranted in immunocompromised patients, for cosmesis, or to prevent autoinnoculation
- Treatment options[2]
- Cryotherapy - liquid nitrogen, dry ice
- Scrub with betadine or retin-A 0.025% gel for 5 minutes daily
- Surgical excision (may cause scarring)
- PO antivirals (e.g. Cidofovir)
Disposition
- Discharge
See Also
External Links
References
- Olsen JR, Gallacher J, Piguet V, Francis NA. Epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum in children: a systematic review. Fam Pract. 2014 Apr;31(2):130-6. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmt075.
- Nandhini G, Rajkumar K, Kanth KS, Nataraj P, Ananthakrishnan P, Arunachalam M. Molluscum Contagiosum in a 12-Year-Old Child – Report of a Case and Review of Literature. Journal of International Oral Health : JIOH. 2015;7(1):63-66.
- Zhuang K, Ran Y, Xu F, Lama J. Atypical infantile genital Molluscum contagiosum. Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia. 2015;90(3):403-405. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153298.
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.