Lymphangitis
Background
- Inflammation of deep dermal/subdermal lymphatic channels
- Usually due to inoculation of skin flora through wound or cellulitis
- Non-infectious lymphangitis much less common, typically due to malignancy
Clinical Features
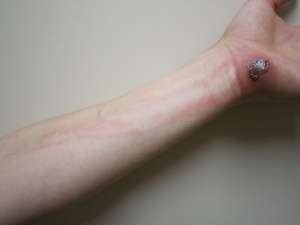
Forearm lymphangitis due to cellulitis of the hand
Another example of lymphangitis
- Pain
- Fever
- Streaking erythema
- Tenderness to palpation
- +/- tender lymphadenopathy
Differential Diagnosis
Skin and Soft Tissue Infection
- Cellulitis
- Erysipelas
- Lymphangitis
- Folliculitis
- Abscess
- Necrotizing soft tissue infections
- Mycobacterium marinum
Evaluation
- Clinical diagnosis
Management
- Depends on underlying case, but usually IV antibiotics, fluids, analgesia
Disposition
See Also
External Links
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.