Legionella
Background
- Gram negative aerobe
- L. pneumophila: associated with two distinct syndromes: pneumonia (legionnaires disease) and Pontiac Fever
- Infection typically occurs via inhalation of aerosolized contaminated water or aspiration of contaminated water
- Outbreaks often associated with cooling towers, hot tubs, medical equipment
- Increased incidence with hot, humid, weather and thundershowers
- Most commonly found in patients age > 50 years, smokers, immunocompromised.[1]
- However, likely underestimated in children[2]
Clinical Features
- Pontiac fever[3]
- Fever, mild flu-like illness
- Absence of pneumonia
- Legionnaires disease[4]
- High mortality
- Incubation 2-10d[5]
- Fever, often high
- Cough
- Respiratory distress
- Respiratory failure in ~10% of all cases[6]
- Relative [[bradycardia (relative to temperature)
- Gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g. nausea/vomiting, diarrhea)
- Neurologic symptoms
Gastrointestinal symptoms Neurologic symptoms Can cause tremor, seizures, Guillain-Barre, and chorea. Has been linked to cases of Acute Cerebellar Ataxia. [Nigro, 1983] Respiratory failure occurs in ~10% of all cases.
Differential Diagnosis
Causes of Pneumonia
Bacteria
- Gram-positive
- Gram-negative
- Atypical pneumonia
- Chlamydophila pneumoniae
- Chlamydophila psittaci
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Coxiella burnetti
- Legionella pneumophila
Viral
- Common
- Influenza
- Respiratory syncytial virus
- Parainfluenza
- Rarer
- Adenovirus
- Metapneumovirus
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
- Middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS)
- 2019-nCoV (COVID-19)
- Cause other diseases, but sometimes cause pneumonia
- Herpes simplex virus
- Varicella-zoster (VZV)
- Measles
- Rubella
- Cytomegalovirus
- Smallpox
- Dengue
Evaluation[7]
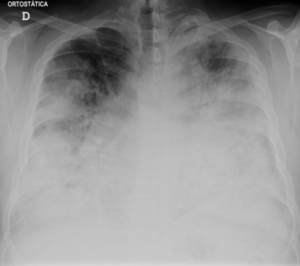
Severe case of Legionellosis on CXR
- Sputum sample for culture
- Urine legionella antigen
- Na: Low in CAP but mostly frequently associated with Legionella
- AST/ALT: Mildly increased 2-5x normal
- Phosphate: Decreased
- CK: Increased
- CRP: > 35
- Ferritin: Increased >2x normal
Management
- Reportable disease, notify appropriate health department[8]
- First line
- Alternatives:
- Doxycycline
- Tigecycline
- Respiratory fluoroquinolone for severe disease[9]
Antibiotic Sensitivities[10]
Key
- S susceptible/sensitive (usually)
- I intermediate (variably susceptible/resistant)
- R resistant (or not effective clinically)
- S+ synergistic with cell wall antibiotics
- U sensitive for UTI only (non systemic infection)
- X1 no data
- X2 active in vitro, but not used clinically
- X3 active in vitro, but not clinically effective for Group A strep pharyngitis or infections due to E. faecalis
- X4 active in vitro, but not clinically effective for strep pneumonia
Table Overview
See Also
References
- Cunha BA. Legionnaires' disease: clinical differentiation from typical and other atypical pneumonias. Infect Dis Clin N Am. 2010;24(1):73-105.
- Yu VL1, Lee TC. Neonatal legionellosis: the tip of the iceberg for pediatric hospital-acquired pneumonia? Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2010 Mar;29(3):282-4.
- https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2020/travel-related-infectious-diseases/legionellosis-legionnaires-disease-and-pontiac-fever
- https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2020/travel-related-infectious-diseases/legionellosis-legionnaires-disease-and-pontiac-fever
- Eison, R. Legionella Pneumonia: When to Suspect, Diagnostic Considerations, and Treatment Strategies for Hospital-Based Clinicians. Curr Emerg Hosp Med Rep (2014) 2: 205.
- https://pedemmorsels.com/legionellosis-in-children/
- Cunha BA. Legionnaires' disease: clinical differentiation from typical and other atypical pneumonias. Infect Dis Clin N Am. 2010;24(1):73-105.
- https://www.cdc.gov/legionella/downloads/case-report-form.pdf
- Burke et Al. Legionnaires Disease Treatment & Management. Aug 18, 2014. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/220163-treatment#d11
- Sanford Guide to Antimicrobial Therapy 2014
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.