Left bundle branch block
Evaluation
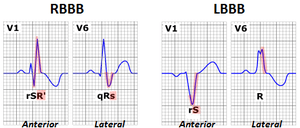
- ST Depression and T wave inversion are common
- QRS > 0.12 in limb leads
- Leads
- Large and wide R waves — leads I, aVL, V5, and V6
- Small R wave followed by deep S wave —leads II, III, aVF, V1–V3
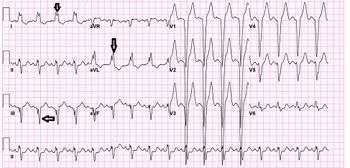
LBBB
Differential Diagnosis
Wide-complex tachycardia
Assume any wide-complex tachycardia is ventricular tachycardia until proven otherwise (it is safer to incorrectly assume a ventricular dysrhythmia than supraventricular tachycardia with abberancy)
- Regular
- Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
- PSVT with aberrant conduction:
- PSVT with bundle branch block^
- PSVT with accessory pathway
- Atrial flutter with bundle branch block^
- Sinus tachycardia with bundle branch block^
- Accelerated idioventricular rhythm (consider if less than or ~120 bpm)
- Metabolic
- Irregular
- Atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter with variable AV conduction AND bundle branch block^
- Atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter with variable AV conduction AND accessory pathway (e.g. WPW)
- Atrial fibrillation + hyperkalemia
- Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
^Fixed or rate-related
See Also
- ECG (Main)
- Sgarbossa's Criteria
- STEMI equivalents
References
- Journal of Electrocardiology. Vol 43 (2010). 40-42.
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.