Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Background
- A congenital heart defect in which the left heart is severely underdeveloped
- Accounts for 2 to 3% of all congenital heart disease [1]
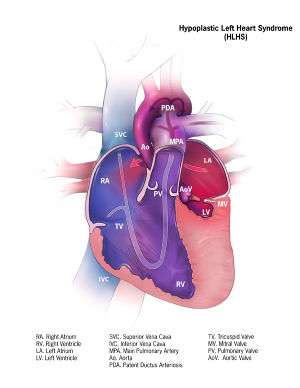
Physiology
- With a diminutive LV, the RV must perfuse both pulmonary and systemic circulations
- Survival is dependent on:
- PDA (for systemic perfusion from RV to the aorta)
- Nonrestrictive ASD to ensure adequate mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
Clinical Features
Infant with cyanosis due to hypoplastic left heart syndrome.
- Asymptomatic at birth because of adequate systemic perfusion through a PDA and initially high pulmonary vascular resistance
- As the PDA begins to close and pulmonary vascular resistance decreases, may develop:
- Symptoms can rapidly progress from cyanosis, increased respiratory distress, and poor feeding to heart failure and cardiogenic shock
Differential Diagnosis
Congenital Heart Disease Types
- Cyanotic
- Acyanotic
- AV canal defect
- Atrial septal defect (ASD)
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
- Cor triatriatum
- Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
- Pulmonary/aortic stenosis
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Differentiation by pulmonary vascularity on CXR[2]
- Increased pulmonary vascularity
- Decreased pulmonary vascularity
- Tetralogy of fallot
- Rare heart diseases with pulmonic stenosis
Evaluation
- ECG
- Right axis deviation, RV hypertrophy
- Chest x-ray
- Cardiomegaly, increased pulmonary vasculature
- Echocardiography
Management
- Stabilize cardiopulmonary function prior to surgery
- Maintain PDA to provide sufficient mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, and adequate systemic perfusion
- Prostaglandin E1
- Start infusion at 0.05 mcg/kg/min IV and titrate up to 0.1 mcg/kg/min, monitoring for hypotension and apnea
- Side Effects: Hypotension, Bradycardia, Seizures and Apnea
- Prostaglandin E1
- Staged surgical repair
- First stage (Norwood procedure) performed in neonates
- SpO2 ranges in mid 70s-80s
- Second stage (bidirectional Glenn procedure) performed at 3-6 months
- SpO2 ranges in mid 70s-80s
- Third stage (Fontan procedure) performed at 18-30 months
- Preload dependent with SpO2 ranging from low to high 90s
- First stage (Norwood procedure) performed in neonates
Disposition
- Admit
See Also
External Links
References
- Gordon BM. Decreasing number of deaths of infants with hypoplastic left heart syndrome. J Pediatr. 2008;153(3):354-8.
- Knipe K et al. Cyanotic congenital heart diseases. Radiopaedia. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/cyanotic-congenital-heart-disease
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.