Stye (hordeolum)
Background
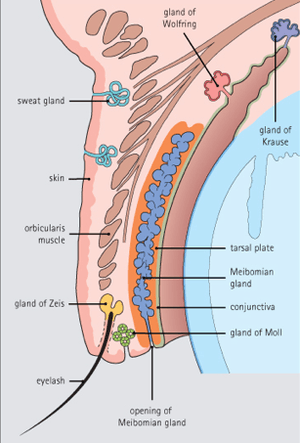
- External - arises from blockage and infection of Zeis (sebaceous) or Moll (sweat) glands
- Internal - arises from blockage and infection of meibomian glands
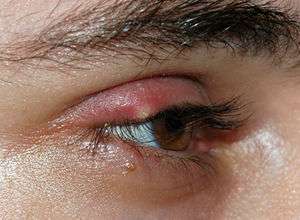
External stye
Internal stye
Clinical Features
- Pustule of eyelid
- Usually accompanied by pain, edema, and erythema
Differential Diagnosis
Proptosis
- Normal IOP
- Orbital cellulitis
- Orbital pseudotumor
- Orbital tumor
- Increased IOP
- Retrobulbar abscess
- Retrobulbar emphysema
- Retrobulbar hemorrhage
- Orbital tumor
No proptosis
- Periorbital cellulitis/erysipelas
- Dacryocystitis (lacrimal duct)
- Dacryocele/Dacryocystocele
- Dacryostenosis
- Dacryoadenitis (lacrimal gland)
- Allergic reaction
- Nephrotic Syndrome (pediatrics)
Lid Complications
- Blepharitis (crusts)
- Chalazion (meibomian gland)
- Stye (hordeolum) (eyelash folicle)
Other
- Subperiosteal abscess
- Orbital abscess
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis
- Conjunctivitis
- Contact dermatitis
- Herpes zoster
- Herpes simplex
- Sarcoidosis
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Evaluation
- Clinical diagnosis, based on history and physical exam
Management
- Warm compresses
- Avoid eye makeup
- Antibiotics
- Consider oral antibiotics (with staph coverage) if patient has concurrent periorbital cellulitis (rare)
- Little evidence that topical antibiotics are helpful
Disposition
- Discharge
- Refer to ophtho if no improvement within 1-2 weeks
See Also
External Links
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.