Glasgow Coma Scale
Scoring
Adult GCS
| Eye Opening | Verbal | Motor |
| 6: Obeys commands | ||
| 5: Oriented | 5: Localizes to pain | |
| 4: Spontaneously opens | 4: Confused speech | 4: Withdraws from pain (normal flexion) |
| 3: Opens to command | 3:Inappropriate words | 3: Decorticate posturing (abnormal flexion) |
| 2: Opens to pain | 2: Incomprehensible sounds | 2: Decerebrate posturing (extension) |
| 1: Does not open | 1: No response | 1: No response |
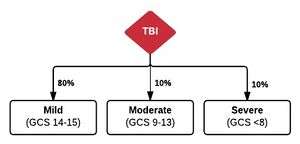
- 14-15: Mild
- 9-13: Moderate
- 3-8: Severe
Pediatric GCS[1][2]
| Eye Opening | Verbal | Motor |
| 6: Normal spontaneous movement | ||
| 5: Smiles, coos, babbles | 5: Withdraws to touch | |
| 4: Opens eyes spontaneously | 4: Irritable, crying (but consolable) | 4: Withdraws to pain |
| 3: Opens eyes to speech only | 3:Inconsolable crying or crying only in response to pain | 3: Abnormal flexion to pain (Decorticate response) |
| 2: Opens eyes to pain only | 2: Moans in response to pain | 2: Abnormal extension to pain (Decerebrate response) |
| 1: Does not open eyes | 1: No response | 1: No response |
Note:
- For Motor score 4, pain is defined flat, fingernail pressure (often performed with the barrel of a pencil).
- For Motor scores 2 and 3, pain is defined by pressing hard on the supraorbital notch. If this unsuccessful, sternal pressure may also be attempted.
See Also
External Links
References
- Holmes JF, Palchak MJ, MacFarlane T, et al. Performance of the pediatric glasgow coma scale in children with blunt head trauma. Acad Emerg Med. 2005 Sep;12(9):814-9.
- James HE. Neurologic evaluation and support in the child with an acute brain insult. Pediatr Ann. 1986 Jan;15(1):16-22.
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.