Gallbladder disease (main)
Background
Gallbladder disease types
- Acute calculous cholecystitis
- Cholangitis (ascending cholangitis)
- Symptomatic cholelithiasis (biliary colic)
- Acalculous cholecystitis
- Choledocholithiasis
Anatomy & Pathophysiology
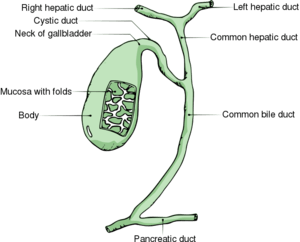
Gallbladder anatomy
- Gallstones are classified as cholesterol stones and pigmented stones (black and brown), and are present in approx 20% of females and 8% of males in the United States
- These stones cause the majority of all biliary tract problems, and depending on where the stone become impacted, specific problems occur.
- Bile flows out the gallbladder, down the cystic duct into the common bile duct, and ultimately into the 1st portion of the duodenum.
Clinical Features
- RUQ pain
- Additional features vary by pathology
Differential Diagnosis
RUQ Pain
- Gallbladder disease
- Peptic ulcer disease with or without perforation
- Pancreatitis
- Acute hepatitis
- Pyelonephritis
- Pneumonia
- Kidney stone
- Pancreatitis
- GERD
- Appendicitis (retrocecal)
- Pyogenic liver abscess
- Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Syndrome
- Hepatomegaly due to CHF
- Herpes zoster
- Myocardial ischemia
- Bowel obstruction
- Pulmonary embolism
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Evaluation
- CBC
- Chemistry
- LFTs
- Lipase
- PT/PTT
- Biliary ultrasound
Management
- Analgesia PRN
- Management varies per specific pathology
Disposition
- Dependant on pathologic process
See Also
References
Video
START_WIDGET1d05835443ffb7ca-0END_WIDGET
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.