Flexor tenosynovitis
Background
- Surgical emergency - flexor sheaths are contiguous with deep spaces of the hand
- Usually associated with a penetrating trauma
Clinical Features
Kanavel's Signs
- Pain with passive extension (often the first sign seen)
- Percussion tenderness (tenderness over entire length of flexor tendon sheath)
- Uniform swelling (symmetric finger swelling along length of the tendon sheath)
- Flexion posture (flexed posture of involved digit at rest to minimize pain)
Differential Diagnosis
Evaluation
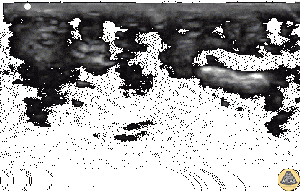
Waterbath POCUS demonstrating fluid collection between tendon and bone[1]
Workup
- CBC
- ESR
- Ultrasound
- Xray
Evaluation
- Generally a clinical diagnosis, based on history and physical exam
- Labs generally show elevated WBC and inflammatory markers
- Xray is done to rule out radiopaque foreign body
Management
- Emergent hand surgery consult in ED
- Antibiotics for most common skin pathogens Strep and Staph (start immediately if suspected but consider obtaining wound culture if any spontaneous drainage is present)
- Vancomycin 1gm IV q12hr AND
- Ampicillin/Sulbactam 1.5gm IV q6h OR cefoxitin 2gm IV q8h OR Piperacillin/Tazobactam 3.375gm IV q6h
- Special Antibiotic Considerations
- Diabetic Patients ensure you have Pseudomonal Coverage by using Piperacillin/Tazobactam rather than Ampicillin/Sulbactam or cefoxitin
- Marine Exposure consider adding a Fluroquinolone, Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim or Doxycycline to cover common marine organisms
Disposition
- Admit
See Also
- Hand infection
External Links
Video
START_WIDGET8990c9c681cb8b3b-0END_WIDGET
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.