Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome
Background
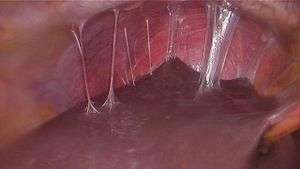
"Violin string sign", adhesions between the liver and abdominal wall.
- A complication of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, involving acute gonococcal or chlamydia trachomatis peritonitis of the right upper quadrant in women
- Pain is caused by liver capsule inflammation
Clinical Features[1]
- Sudden onset of severe right upper quadrant abdominal pain
- Distal pleuritic component +/- radiation to the shoulder
- May not have symptoms of PID
Differential Diagnosis
RUQ Pain
- Gallbladder disease
- Peptic ulcer disease with or without perforation
- Pancreatitis
- Acute hepatitis
- Pyelonephritis
- Pneumonia
- Kidney stone
- Pancreatitis
- GERD
- Appendicitis (retrocecal)
- Pyogenic liver abscess
- Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Syndrome
- Hepatomegaly due to CHF
- Herpes zoster
- Myocardial ischemia
- Bowel obstruction
- Pulmonary embolism
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Evaluation
Management
- Fully treat pelvic inflammatory disease
Disposition
- Admission criteria same for PID
- Pregnancy
- Toxic, systemic symptoms
- Poor compliance
- Failure of outpatient therapy
- Tubo-ovarian abscess
See Also
- PID
References
- Livengood et al. Clinical features and diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease. Uptodate.
- Curtis AH. A cause of adhesion in the right upper quadrant.JAMA. 1930;94(16):1221-1222. doi:10.1001/jama.1930.02710420033012.
- Peter, N. G.; Clark, L. R.; Jaeger, J. R. (2004). "Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome: a diagnosis to consider in women with right upper quadrant pain". Cleveland Clinic journal of medicine 71 (3): 233–239. doi:10.3949/ccjm.71.3.233. PMID 15055246
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.