Esophageal candidiasis
Background
- Most commonly seen in HIV patients with CD4 count < 100 (AIDS-defining illness) or chronic inhaled glucocorticoid use
Clinical Features[1]
- Odynophagia
- Dysphagia
- Retrosternal pain
- Nausea/vomiting
Differential Diagnosis
Esophagitis
- Esophageal candidiasis
- CMV esophagitis
- HSV esophagitis
- Eosinophilic esophagitis
- Medication-induced esophagitis
Evaluation
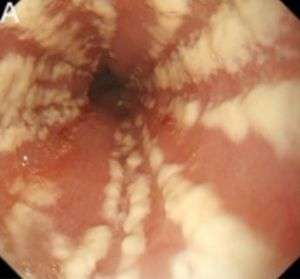
Esophageal Candidiasis
- Thick, white, linear esophageal plaques on endoscopy
Management
- Fluconazole 400mg PO loading dose, followed by 200mg PO Qdaily x 2 weeks
- Itraconazole 200mg PO Qdaily for 2 weeks
- has more nausea side-effects and drug interactions compared to fluconazole
Disposition
See Also
External Links
References
- Kauffmann CA. Overview of Candida Infections. UptoDate. 2016.
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.