Dry gangrene
Background
Gangrene General Info
- A form of tissue necrosis characterized by critically insufficient blood supply leading to tissue death.
- Primarily divided into wet gangrene vs dry gangrene. Other, specific forms of gangrene include Fournier's gangrene, gas gangrene, and necrotizing fasciitis.
- Most commonly occur in distal extremities, clasically the feet.
- Main risk factors are diabetes, smoking, and peripheral arterial disease.
Clinical Features
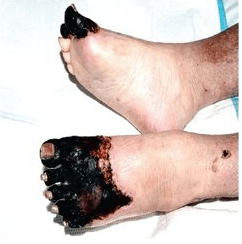
- Usually due to peripheral arterial disease, but can also be caused by acute limb ischemia.
- Presents with dry, shrunken tissue, usually ranging from dark red to completely black, often with a clear line of demarcation between healthy and necrotic tissue.
- Typically not painful.
Differential Diagnosis
Evaluation
- History and physical examination are usually sufficient to make the diagnosis.
- If acute limb ischemia is suspected, consider a CTA of the affected limb and a vascular surgery consultation.
Management
- Infection rarely present
- Keep area clean and dry to prevent infection
- Will usually auto-amputate in <6mo
- Refer to vascular surgery in case fails to auto-amputate; may benefit from revascularization therapy to prevent further tissue death
- If acute limb ischemia is present, embolectomy or surgical bypass may be required to restore flow.
Disposition
- Outpatient, if acute limb ischemia is NOT a concern
See Also
External Links
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.