Drug rash
Background
ABCs of Drug Rashes
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)
- Bullous disease, drug induced
- Captopril (ACE-inhibitor) induced angioedema
- Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome
- SJS/TEN
Clinical Features
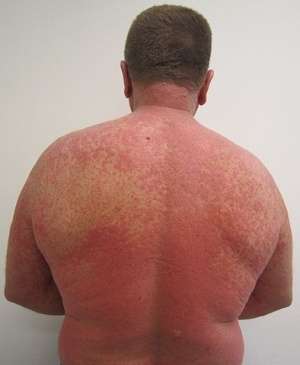
Morbilliform drug eruption on back
- Sudden, usually morbilliform, often starts on face & trunk & spreads
- More polymorphous than viral exanthem
Differential Diagnosis
Erythematous rash
- Positive Nikolsky’s sign
- Febrile
- Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (children)
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis/SJS (adults)
- Afebrile
- Febrile
- Negative Nikolsky’s sign
Evaluation
- Typically a clinical diagnosis
Table of Severe Drug Rashes
| Charateristic | DRESS | SJS/TEN | AGEP | Erythroderma |
| Image | 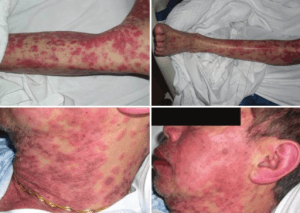 |  | 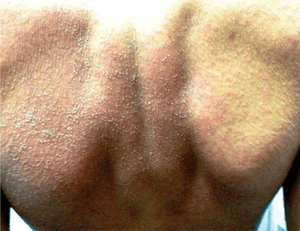 | _Skin_Syndrome_-_Feet_Collage.jpg) |
| Onset of eruption | 2-6 weeks | 1-3 weeks | 48 hours | 1-3 weeks |
| Duration of eruption (weeks) | Several | 1-3 | <1 | Several |
| Fever | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| Mucocutaneous features | Facial edema, morbilliform eruption, pustules, exfoliative dermattiis, tense bullae, possible target lesions | Bullae, atypical target lesions, mucocutaneous erosions | Facial edema, pustules, tense bullae, possible target lesions, possibl emucosal involvement | Erythematous plaques and edema affecting >90% of total skin surface with or without diffuse exfoliation |
| Lymph node enlargement | +++ | - | + | + |
| Neutrophils | Elevated | Decreased | Very elevated | Elevated |
| Eosinophils | Very elevated | No change | Elevated | Elevated |
| Atypical lymphocytes | + | - | - | + |
| Hepatitis | +++ | ++ | ++ | - |
| Other organ involvement | Interstitial nephritis, pneumonitis, myocarditis, and thydoiditis | Tubular nephritis and tracheobronical necrosis | Possible | Possible |
| Histological pattern of skin | Perivascular lymphocytcic infiltrate | Epidermal necrosis | Subcorneal pustules | Nonspecific, unless reflecting Sezary syndrome or other lymphoma |
| Lymph node histology | Lymphoid hyperplasia | - | - | No, unless reflecting Sezary syndrome or other malignancy |
| Mortality (%) | 10 | 5-35 | 5 | 5-15 |
Management
- Discontinue offending agent
- Supportive
- Topical steroids may help relieve pruritus
Disposition
- If no signs of anaphylaxis or significant sloughing, consider outpatient management
See Also
External Links
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.