Corneal ulcer
Background
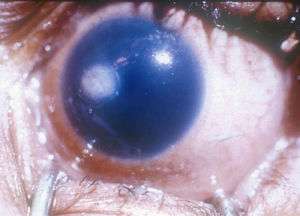
Corneal ulcer without infection
- Major cause of impaired vision and blindness worldwide
- Break in epithelial layer allows infectious agents to gain access to the underlying stroma
- Risk factors include: incomplete lid closure (e.g. secondary to Bell's palsy) and soft contact lens use (especially sleeping in contacts)
Causes
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Herpes simplex
- Varicella-zoster
- Fungi
- Candida
- Aspergillus
- Penicillium
- Cephalosporium
Clinical Features
- Redness and swelling of lids and conjunctiva
- Ocular pain or foreign body sensation
- Decreased visual acuity (if located in central visual axis or uveal tract is inflamed)
- Photophobia
- Gray/white corneal lesion (will have fluorescein uptake)
- Requires careful physical exam as 40% of lesions < 5mm
- Hypopyon may be present
- Iritis signs may be present (miotic pupil, consensual photophobia)
Complications
- Corneal scarring
- Corneal perforation
- Anterior/posterior synechiae
- Glaucoma
- Cataracts
Differential Diagnosis
Unilateral red eye
- Acute angle-closure glaucoma^
- Anterior uveitis
- Conjunctivitis
- Corneal erosion
- Corneal ulcer^
- Endophthalmitis^
- Episcleritis
- Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
- Inflamed pinguecula
- Inflamed pterygium
- Keratoconjunctivitis
- Keratoconus
- Nontraumatic iritis
- Scleritis^
- Subconjunctival hemorrhage
- Orbital trauma
^Emergent diagnoses
^^Critical diagnoses
Evaluation
- Clinical
Management
- Emergent ophtho consultation
- Topical antibiotics
- Vigamox 1 drop qhour OR
- Ciprofloxacin 1 drop qhour
- Consider antiviral or antifungal if high suspicion for viral or fungal cause (rare)
- Cycloplegic may help if iritis present
- Do not patch the eye
Disposition
- Discharge with ophtho followup within 24-48 hours
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.