Congenital heart disease
Background
Congenital Heart Disease Types
- Cyanotic
- Acyanotic
- AV canal defect
- Atrial septal defect (ASD)
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
- Cor triatriatum
- Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
- Pulmonary/aortic stenosis
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Differentiation by pulmonary vascularity on CXR[1]
- Increased pulmonary vascularity
- Decreased pulmonary vascularity
- Tetralogy of fallot
- Rare heart diseases with pulmonic stenosis
Clinical Features
| Clinical Presentation | Causative Conditions in Neonates | Causative Conditions in Infants and Children |
| Cyanosis | Transposition of the great arteries, TOF, tricuspid atresia, truncus arteriosus, total anomalous pulmonary venous return | TOF, Eisenmenger complex |
| Cardiovascular shock | Critical aortic stenosis, coarctation of the aorta, HLHS | Coarctation of the aorta (infants) |
| Congestive heart failure | Rare: PDA, HLHS | PDA, VSD, ASD, atrioventricular canal |
| Murmur | PDA, valvular defects (AS, PS) | VSD, ASD, PDA, outflow obstructions, valvular defects (AS, PS) |
| Syncope | — | AS, PS, Eisenmenger complex |
| Hypertension | — | Coarctation of the aorta |
| Arrhythmias | — | ASD, Ebstein anomaly, postsurgical complication after repair of congenital heart defect |
Differential Diagnosis
Sick Neonate
THE MISFITS [2]
- Trauma
- Heart
- Congenital heart disease
- Hypovolemia
- Endocrine
- Metabolic
- Sodium
- Calcium
- Glucose
- Inborn errors of metabolism
- Seizure
- Formula / feeding problems
- Intestinal Disasters
- Toxin
- Sepsis
Evaluation
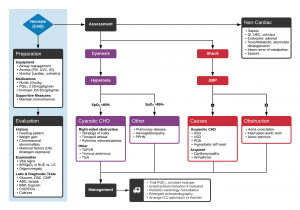
Algorithm for the Evaluation and Management of Suspected Congenital Heart Disease in Neonates
Cyanotic
| Cardiac Lesion | Chest Radiograph | ECG |
| Tetralogy of Fallot | Boot-shaped heart, normal-sized heart, decreased pulmonary vascular markings | Right axis deviation, right ventricular hypertrophy |
| Transposition of the great arteries | Egg-shaped heart, narrow mediastinum, increased pulmonary vascular marking | Right axis deviation, right ventricular hypertrophy |
| Total anomalous pulmonary venous return | Snowman sign, significant cardiomegaly, increased pulmonary vascular markings | Right axis deviation, right ventricular hypertrophy, right atrial enlargement |
| Tricuspid atresia | Heart of normal to slightly increased size, decreased pulmonary vascular markings | Superior QRS axis with right atrial hypertrophy, left atrial hypertrophy, left ventricular hypertrophy |
| Truncus arteriosus | Cardiomegaly, increased pulmonary vascular markings | Biventricular hypertrophy |
Acyanotic (duct-dependent)
| Coarctation of the aorta | Cardiomegaly with pulmonary edema (neonate) | RVH, right bundle-branch block (neonate) |
| Rib notching and collateral vascularity (child) | LVH (child) | |
| Hypoplastic left heart syndrome | Cardiomegaly | Right atrial enlargement, RVH, peaked P waves |
| Aortic stenosis | Cardiomegaly | LVH in severe cases |
Acyanotic non-duct dependent (i.e. CHF)
| Atrial septal defect | Cardiomegaly with increased vascular markings | Right axis deviation, RVH, RBBB |
| VSD | Cardiomegaly with increased vascular markings | LAH, LVH, (RVH with larger VSDs) |
| PDA | Cardiomegaly with increased vascular markings | LVH, RVH with larger PDAs |
| Endocardial cushion defect | Cardiomegaly with increased vascular markings | Superior QRS axis with RVH, RBBB, LVH, prolonged PR interval |
| Anomalous origin of the left coronary artery | Cardiomegaly | Abnormally deep and wide Q waves with precordial ST segment changes |
Management
Shock (duct-dependent lesion)
- PGE1 0.1mcg/kg/min IV/IO
- Side Effects:
- Apnea (intubate)
- Hypotension
- Bradycardia
- Flushing
- Apnea (intubate)
- Side Effects:
- NS 10cc/kg
- Dobutamine
Tet Spell
- Knee chest position
- Increased venous return to heart, increased SVR (decreased R>L shunting)
- O2
- Morphine or NS to increase preload
- Sodium bicarbonate 2mEq/kg IV bolus (promotes vasodilation)
- Propranolol 0.2mg/kg IV (relieves infundibular spasm)
- Phenylephrine 2-10mcg/kg/min to increased SVR
CHF
- O2 (give only if SpO2 <95%)
- Furosemide 1-2mg/kg IV
- Dopamine 5-10mcg/kg/min
- Dobutamine 5-10mcg/kg/min
Thrombolysis for Surgical Shunt Obstruction
- Blalock-Taussig shunt should maintain flow murmur
- Loss of flow murmur alongside profound hypoxia relative to baseline saturations should prompt consideration for shunt obstruction
- Definitive treatment is surgical, but systemic recombinant tPA may be considered as salvage intervention when other options are not readily available[3]
- Heparin bolus 50-100 u/kg
- Notify cardiology, CT surgeon, ECMO
- 0.01 mg/kg bolus r-tPA, then 0.03 - 0.06 mg/kg/hr
Disposition
See Also
References
- Knipe K et al. Cyanotic congenital heart diseases. Radiopaedia. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/cyanotic-congenital-heart-disease
- Brousseau T, Sharieff GQ. Newborn emergencies: the first 30 days of life. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2006 Feb;53(1):69-84, vi.
- Diaz F et al. Systemic thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute life-threatening Blalock-Taussig shunt obstruction. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2016 Jul; 20(7): 425–427.
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.