Calcaneus fracture
Background
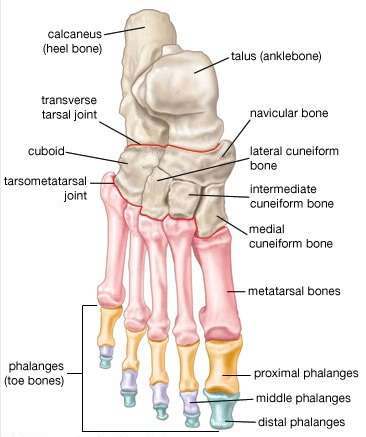
Bones of the foot.
- Associated injuries are common
Types
- Intra-articular (75%)
- Sclerotic line may be only evidence of impacted fracture
- Extra-articular (25%)
- Anterior process fracture is most common
Clinical Features
- Foot pain after trauma - often from axial load such as fall from height or motor vehicle accident
Differential Diagnosis
Evaluation
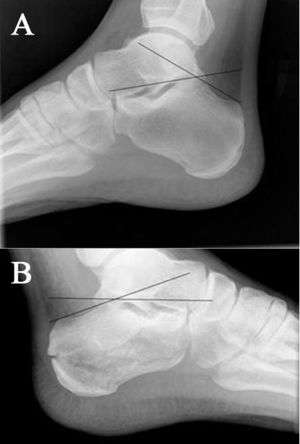
(A) Normal Boehler's angle and (B) Abnormal Boehler's angle
- Plain X-ray imaging
- Decreased Boehler's angle (<25') may be only sign of fracture (compare with opposite side)
- Harris view to tuberosity
Management & Disposition
General Fracture Management
- Acute pain management
- Open fractures require immediate IV antibiotics and urgent surgical washout
- Neurovascular compromise from fracture requires emergent reduction and/or orthopedic intervention
- Consider risk for compartment syndrome
Intra-articular fracture
- Immobilization with posterior ankle splint
- Non-weight bearing
- Elevation (very important - fracture has high rate of severe swelling)
- Ortho consult
Extra-articular fracture
- Immobilization with posterior ankle splint
- Close ortho follow up
See Also
Video
START_WIDGET337d6e39ee61f777-0END_WIDGET
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.