Chest X-ray interpretation
ABC Method
- Airways - ex. FB, trachea deviation
- Bones and soft tissue - ex. Rib fractures, clavicle fracture
- Cardiac - ex. Cardiomegaly
- Diaphragm - ex. Free air
- Effusions - ex. Pleural effusion
- Fields and Fissures - ex. Congestion, consolidations
- Great vessels - ex. Apical cap
- Hila and mediastinum - Widened mediastinum
- Impression
DRSABCDE Method
- Details
- Info of patient
- PA/AP, Lateral
- RIPE - Image quality
- Rotation
- Inspiration
- Picture
- Exposure
- Soft tissues and bones
- Airway & mediastinum
- Breathing
- Lung fields
- Circulation
- Heart position and size
- Diaphragm
- Extras
- Lines, tubes, catheters
Examples
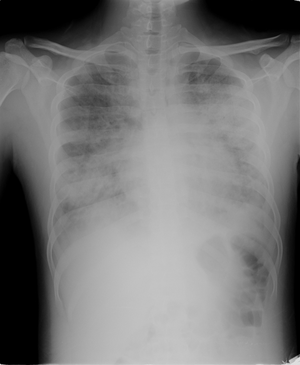
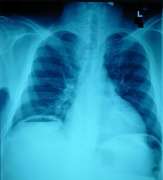 Pneumoperitoneum
Pneumoperitoneum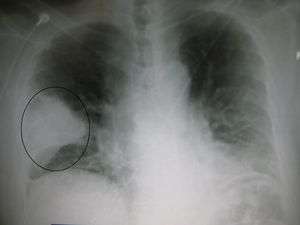 Prominent wedge-shape area of airspace consolidation in the right lung, characteristic of bacterial pneumonia
Prominent wedge-shape area of airspace consolidation in the right lung, characteristic of bacterial pneumonia- Esophageal foreign body (penny in 12 mo male)
 Right sided pneumothorax
Right sided pneumothorax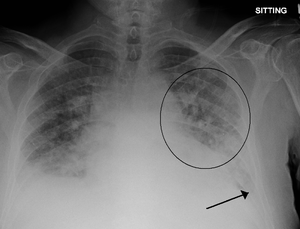 Pulmonary edema with small pleural effusions on both sides.
Pulmonary edema with small pleural effusions on both sides.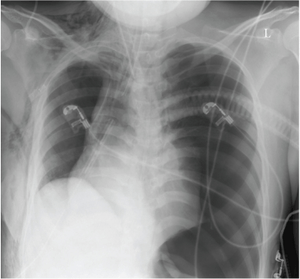 Left sided tension pneumothorax with mediastinal shift
Left sided tension pneumothorax with mediastinal shift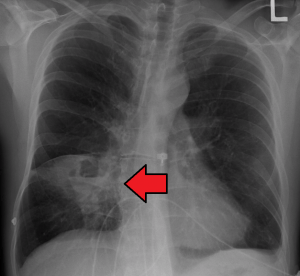
Special Findings
Elevated Hemidiaphram
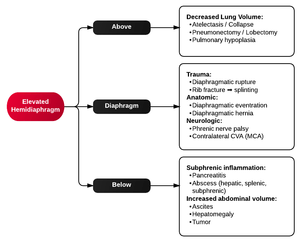
Elevated hemidiaphragm algorithm
See Also
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.