Buprenorphine
Administration
- Type: Opioid- maintenance therapy in opioid use disorder, rapid detox
- Dosage Forms: injectable solution, sublingual tablet
- Dosage Strengths: injectable solution: 0.3 mg/mL; sublingual tablet: 2, 8mg
- Routes of Administration: Buccal, sublingual, intradermal, transdermal, IV, IM
- Common Trade Names: Suboxone (buprenorphine + naloxone), Buprex
Adult Dosing
Highly variable dependent on individual
- Initial dose for patients with Clinical Opioid Withdrawal Scale (COWS) >8: 4mg, observe 45min, redose if COWS remains >8 *Suboxone initial induction dose: 2mg/0.5mg or 4mg/1mg, titrate up by 2-4mg q2h based on withdrawal symptoms up to 8mg/1mg[1]
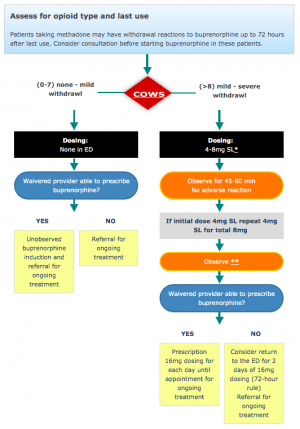
NIH National Institute on Drug Abuse ED Buprenorphine algorithm[2]
Pediatric Dosing
Variable
Special Populations
- Pregnancy Rating: C
- Lactation risk: Infant risk has been demonstrated
- Hepatic dosing: reduce dose or do not use in moderate - severe impairment
- Renal dosing:
Contraindications
- Allergy to class/drug
- SBO, paralytic ileus
- Acute/severe asthma (if unmonitored), respiratory depression
Adverse Reactions
Serious
- Hypotension, prolonged QT, MI
- Respiratory depression
- SBO
- Hepatotoxicity
- Stroke
- Sedation, coma
- Drug dependence or withdrawal
Common
- Pruritus
- Constipation, nausea, diarrhea, xerostomia
- Dizziness, headache, somnolence
- URI symptoms
Pharmacology
- Half-life: 24-48 hours
- Metabolism: Extensive hepatic, CYP3A4 substrate
- Excretion: Mostly fecal, some renal
Mechanism of Action
- Mixed opiate agonist-antagonist, partial mu-opioid agonist, kappa-opioid antagonist
Comments
- No DATA 2000 Waiver (aka X Waiver) required to administer within the ED for up to 72h (e.g. patient can come back to ED for daily dose for 3 days)[3]
See Also
References
- Suboxone prescribing pamphlet https://www.suboxone.com/hcp/induction-phase
- https://d14rmgtrwzf5a.cloudfront.net/sites/default/files/algorithm.pdf
- https://www.drugabuse.gov/nidamed-medical-health-professionals/discipline-specific-resources/initiating-buprenorphine-treatment-in-emergency-department/frequently-asked-questions-about-ed-initiated-buprenorphine
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.