Bacterial conjunctivitis
Background
- Often due to staphylococcus or streptococcus
Clinical Features
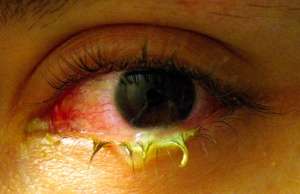
- Painless, unilateral or bilateral mucopurulent discharge
- Often causes adherence of the eyelids on awakening
- Chemosis is common
Differential Diagnosis
Evaluation
Workup
- Eye exam
- Fluorescein stain of cornea (especially in infants) to assess for corneal lesion
- Culture: if severe
Evaluation
Clinical diagnosis of conjunctivitis
| Bacterial | Viral | Allergic | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bilateral | 50% | 25% | Mostly |
| Discharge | Mucopurulent | Clear, Watery | Cobblestoning, none |
| Redness | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Pruritis | Rarely | Rarely | Yes |
| Additional | Treatment: Antibiotics | Treatment: Hygiene | Seasonal |
Management
- Treatment for bacterial organisms is targeted toward S. aureus, S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, Pseudomonas, N. gonorrhea, C. trachomatis
- Contact lens wearers should be given coverage for pseudomonas with one of the fluoroquinolone drops
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
- Counsel patient/family on importance of hand hygiene/avoiding touching face to prevent spread!
These options do not cover gonococcal or chlamydial infections
- Polymyxin B/Trimethoprim (Polytrim) 2 drops every 6 hours for 7 days OR
- Erythromycin applied to the conjunctiva q6hrs for 7 days OR
- Levofloxacin 0.5% ophthalmic solution 1-2 drops every 2 hours for 2 days THEN every 6 hours for 5 days OR
- Moxifloxacin 0.5% ophthalmic 1-2 drops every 2 hours for 2 days THEN every 6 hours for 5 days OR
- Gatifloxacin 0.5% ophthalmic solution 1-2 drops every 2 hours for 2 days THEN 1 drop every 6 hours for 5 days OR
- Azithromycin 1% ophthalmic solution 1 drop BID for 2 days THEN 1 drop daily for 5 days
NB: levofloxacin is preferred for contact lens wearers for coverage of pseudomonas. Advise not to wear contacts for duration of treatment
Chlamydial
- Doxycycline 100mg PO BID for 7 days OR
- Azithromycin 1g (20mg/kg) PO one time dose
- Newborn Treatment: Azithromycin 20mg/kg PO once daily x 3 days
- Disease manifests 5 days post-birth to 2 weeks (late onset)
Gonococcal
- Due to increasing resistance, CDC recommends dual therapy with Ceftriaxone and Azithromycin (even if patient is negative for Chlamydia).
- Ceftriaxone 250mg IM one dose PLUS
- Azithromycin 1g PO one dose
- Newborn Treatment:
- Prophylaxis: Erythromycin ophthalmic 0.5% x1
- Disease manifests 1st 5 days post delivery (early onset)
- Treatment Ceftriaxone 25-50mg IV or IM, max 125mg
Disposition
- Discharge with ophtho follow-up (if no improvement) in 3 - 4 days
See Also
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.