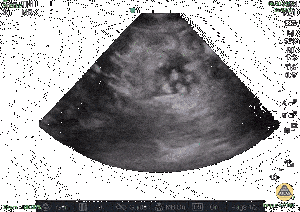
Ascites
Background
- Abnormal buildup of peritoneal fluid
Clinical Features
- Abdominal distention +/- discomfort
- Fluid wave
- +/- SOB if massive amount
Complications
- SBP
- Hepatorenal syndrome
- Portal vein thrombosis/splenic vein thrombosis
Differential Diagnosis
Ascites
- Hepatitis or cirrhosis (most common)
- Heart failure or constrictive pericarditis
- Malignancy (primary or metastatic peritoneal carcinoma)
- Pancreatitis
- Vasculitis
- Connective tissue disorders
- Chylous ascites
Evaluation
- Ascites in females with no other reason for it = gyn neoplasm until proven otherwise (ovarian cancer)
SBP Work-Up of Ascitic Fluid via Paracentesis
- Cell count with differential
- Gram stain
- Culture (10cc in blood culture bottle)
- Glucose
- Protein
Management
- Salt restriction
- Effective in about 15% of patients
- Diuretics
- Spironolactone
- Starting dose = 100mg/day PO (max 400mg/day)
- 40% of patients will respond
- Furosemide
- 40mg/day PO (max 160mg/day)
- Ratio of 100:40 with spironolactone (reduces risks of potassium prob)
- Spironolactone
- Water restriction
- Paracentesis
- Consider liver transplantation and shunting
Disposition
- Frequently outpatient, once SBP is ruled out, if a known reason for ascites and sufficiently therapeutically drained
See Also
- Jaundice
- Paracentesis
- SBP
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.