Acute arterial ischemia
Background
- Sudden decrease in perfusion that may result in irreversible limb loss
- Etiology may be thrombotic or embolic
- Thrombosis occurs in vessels with existing atherosclerosis
- Generally have formed collateral circulation
- Embolism occurs in vessels usually free of atherosclerosis
- Generally do not have existing collateral circulation
- Results in higher level of limb ischemia than thrombosis
- Thrombosis occurs in vessels with existing atherosclerosis
Clinical Features
6 Ps
- Pain - claudication or pain with leg elevation, typically earliest sign
- Paraesthesia - with weakness are early findings and preservation of light touch is good guide to viability
- Pallor
- Paralysis
- Pulselessness - late finding, helpful only if accompanied by skin changes
- Poikilothermia - late finding
Differential Diagnosis
Blue Digit
- Acute peripheral artery disease
- Atheroembolism (AKA Blue Toe Syndrome)
- Arterial embolism
- Arterial thrombosis
- Vasospastic Disorders
- Raynaud’s disease
- Primary erythromelalgia
- Autoimmune
- Idiopathic
- Thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger's disease)
- Chronic peripheral artery disease
- Atherosclerosis obliterans
Acute
- Foot and toe fractures
- Subtalar dislocation
- Metatarsophalangeal sprain (turf toe)
- Acute arterial ischemia
- Calcaneal bursitis
Subacute/Chronic
- Diabetic foot infection
- Peripheral artery disease
- Plantar fasciitis
- Trench foot
- Ingrown toenail
- Paronychia
- Tinea pedis
- Morton's neuroma
- Diabetic neuropathy
Evaluation
Ankle-brachial index (ABI)
- How to measure:
- Position patient supine
- Measure SBP from both brachial arteries using cuff and handheld Doppler over the AC fossa
- Measure SBP from both DP and PT arteries using cuff placed just proximal to the malleoli with Doppler over artery (5-8% of normal patients have absent DP pulse)
- Calculate ABI on each leg by taking the highest ankle SBP (between DP and PT) on that leg divided by the highest brachial SBP and record to 2 decimal places
| ABI | Meaning |
| <0.40 | Severe occlusion |
| 0.40–0.69 | Moderate occlusion |
| 0.70–0.90 | Mild occlusion |
| 0.91–1.30 | Normal |
| >1.30 | Poorly compressible/calcified vessels |
Imaging
- Formal angiogram considered gold standard
- CTA as a diagnostic is near the level of formal angiography
- US is sensitive for proximal extremity occlusions, but sensitivity markedly falls off distally and is operator dependent
Thrombosis vs Embolus
| Key features | Thrombosis | Embolus |
| Source | Usually unknown | Heart (A-fib most common) |
| History | PAD, claudication | Less likely to have PAD and claudication |
| Physical exam | Absent pulse. Consistent with PAD: hair loss, thickened nails etc | Absent pulse. Usually no evidence of PAD |
| Degree of arthersclerosis | Diffuse | Minimal |
| Collaterals | Well-developed | Few |
Rutherford Classification
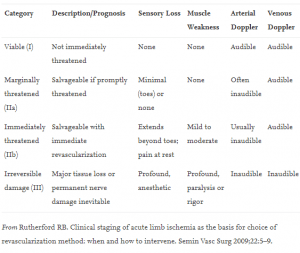
Rutherford Classfication
Management
- Unfractionated heparin
- 80 units/kg bolus → 18units/kg/hr gtt
- ASA
- Dependent positioning
- Pain control
- Vascular surgery consultation (clot retrieval, balloon angioplasty, intraarterial tPA, stenting, bypass)
- Management of embolism = embolectomy (limb salvage decreases after 4-6 hours)
- Management of thrombus = intra-arterial thrombolysis (if non-limb threatening), thrombectomy (if limb-threatening ischmia)
- Interventional radiology if delay in vascular surgery intervention or if unavailable
Disposition
- Admit
See Also
External Links
References
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.