Acute alveolar osteitis
Background
- Osteomyelitis of exposed bone. Also known as "Dry socket"
- Caused by premature loss of healing clot in the alveolar socket after tooth extraction[1]
- Occurs 2-4d after tooth extraction
- Initial post-extraction pain subsides followed by sudden/severe pain at extraction site
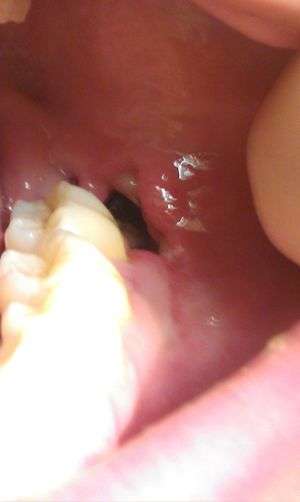
Dry socket
Clinical Features
- Postoperative pain at site of recent tooth extraction
Differential Diagnosis
Evaluation
- Clinical diagnosis
- Exposed bone with no clot in extraction site
Management
- Analgesia (often requires dental block)
- Irrigate but socket should not be curetted and any residual clot should not be removed
- Pack with iodoform ribbon gauze soaked with eugenol (oil of cloves) or local anesthetic
- If available, may use commercially available "dry socket paste"
- Penicillin VK 500mg PO QID OR clindamycin 300mg PO QID
Disposition
- Discharge with dental follow-up within 24 hours
See Also
References
- Kolokythas A, Olech E, Miloro M. Alveolar Osteitis: A Comprehensive Review of Concepts and Controversies. International Journal of Dentistry. 2010; 2010: 249073. doi:10.1155/2010/249073
This article is issued from
Wikem.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.